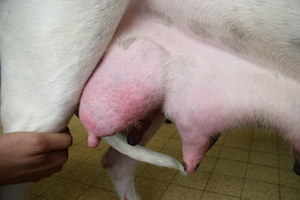
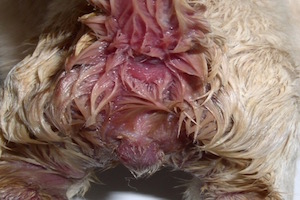
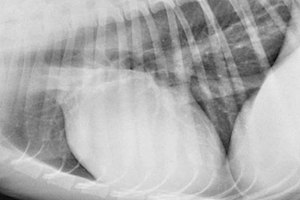
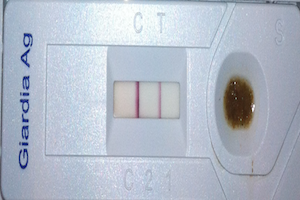
Canine herpesvirus and obstetrical consequences
Canine herpes virus is an enveloped virus, which can be transmitted by transplacental, venereal (semen, vaginal secretions) and oro-nasal routes.
It is therefore a sexually transmitted disease.
Abortion products (fetuses, fetal envelopes) can also be contaminants.